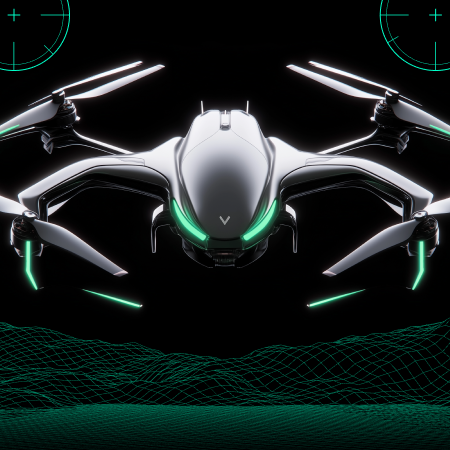
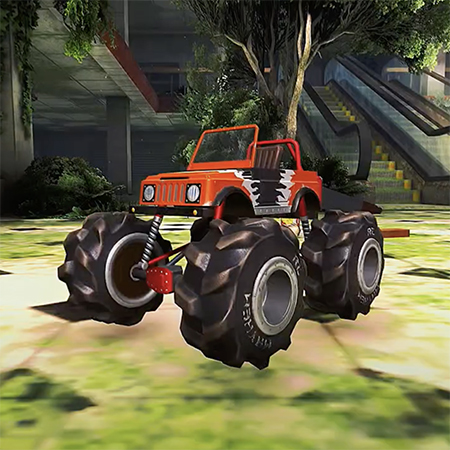
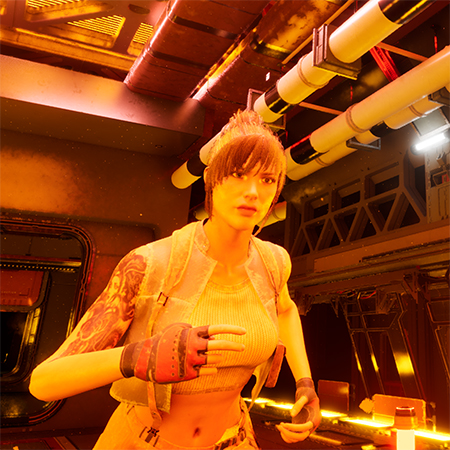
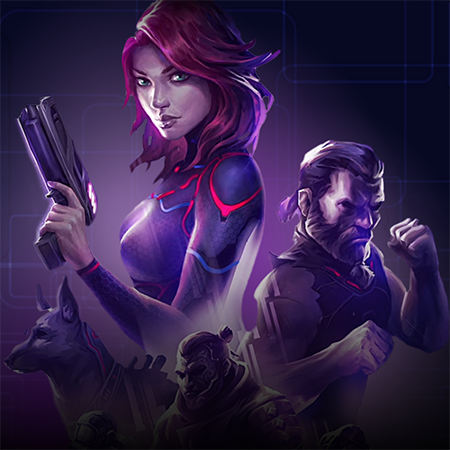
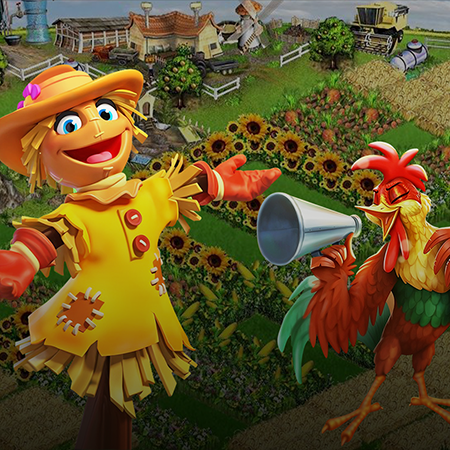
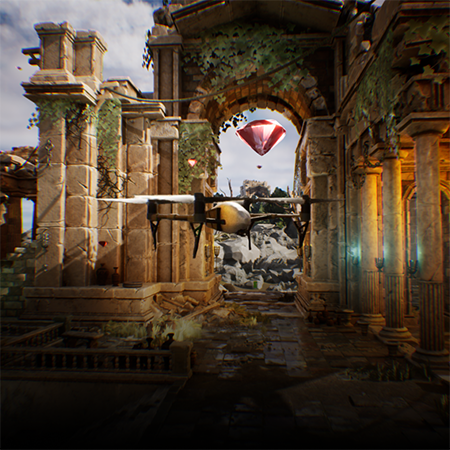
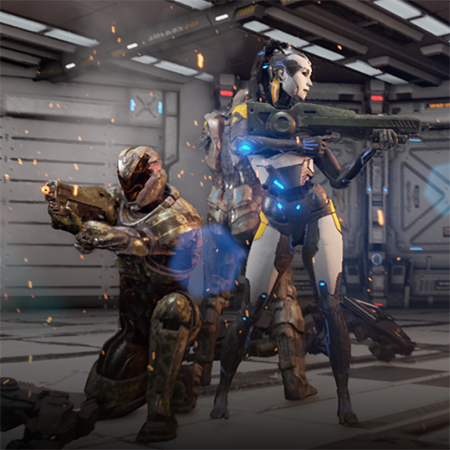
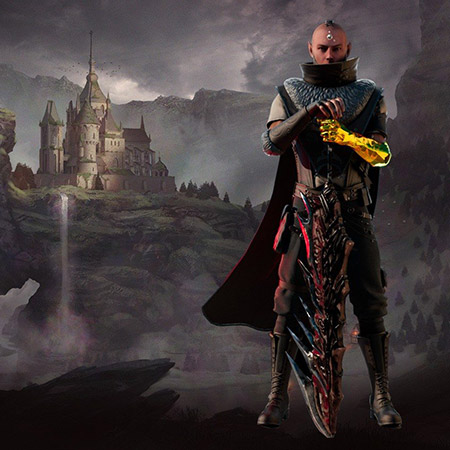
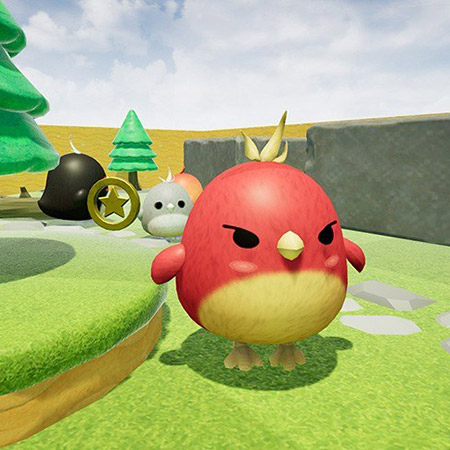
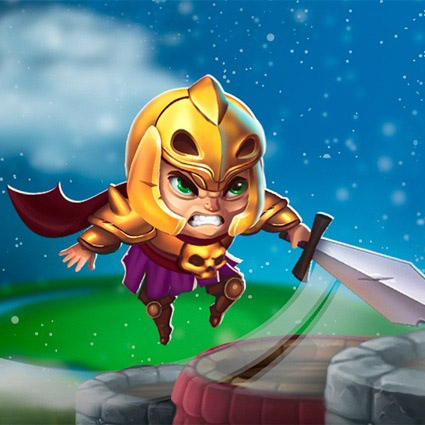
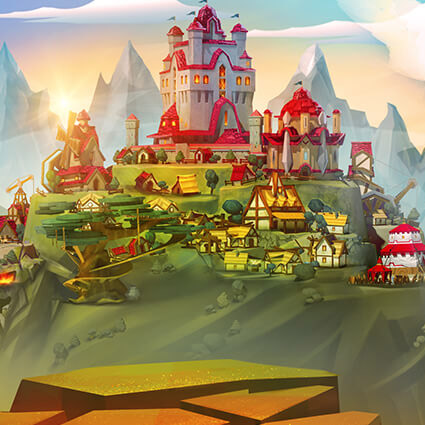
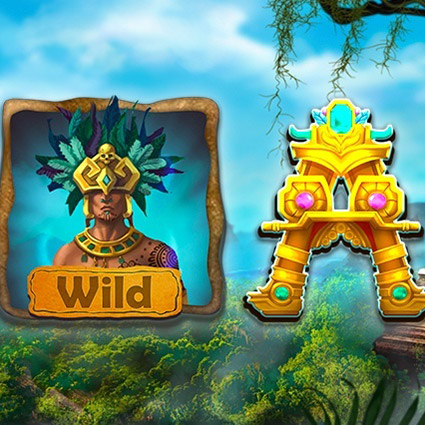
Nomadland is a play-to-earn NFT turn-based strategy whose narrative occurs in a world where players can buy land, build farms, and fight epic monsters. Another key element of this game is that a player not only can fight enemies but also capture them, upgrading their ranks as well as producing weapons and armors as they battle against other gamers.

CORE GAMEPLAY MECHANICS
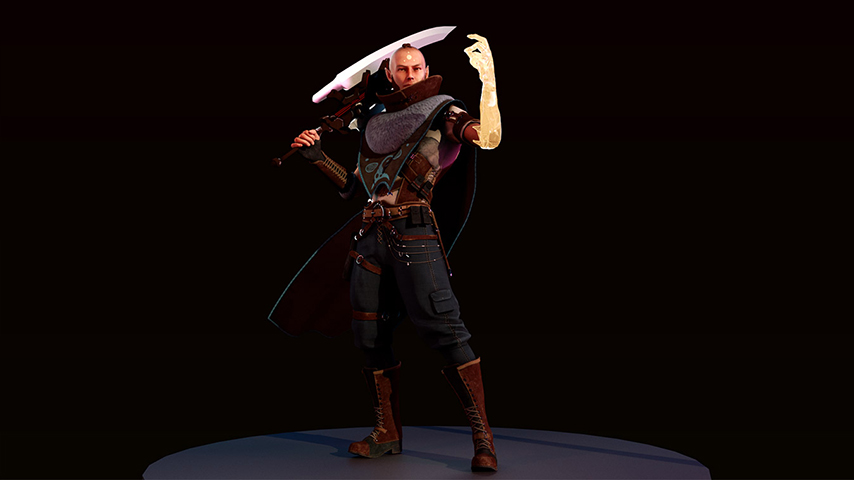
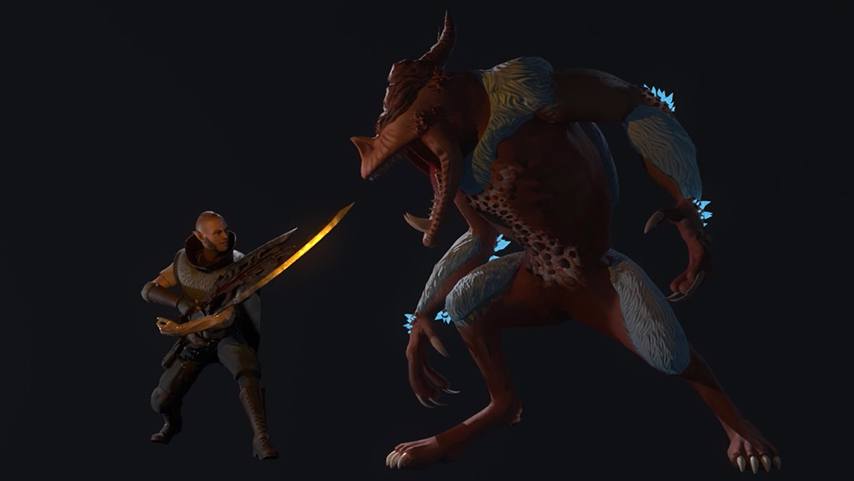
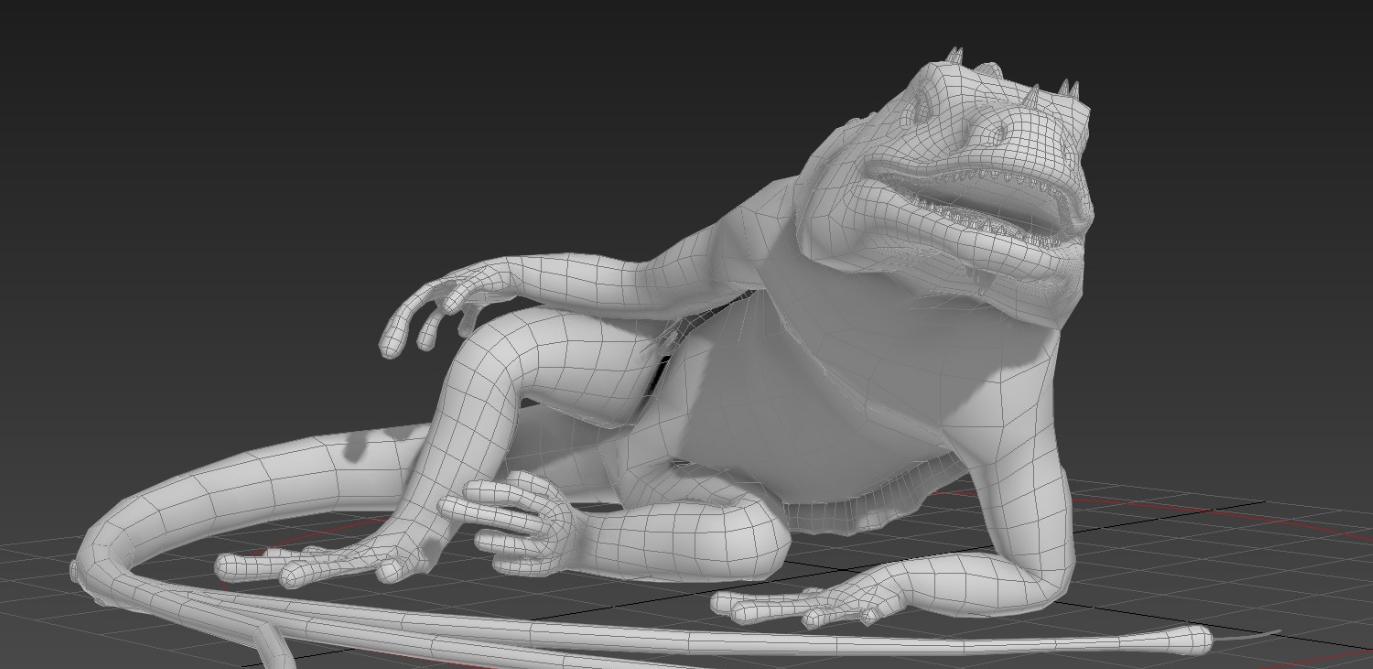
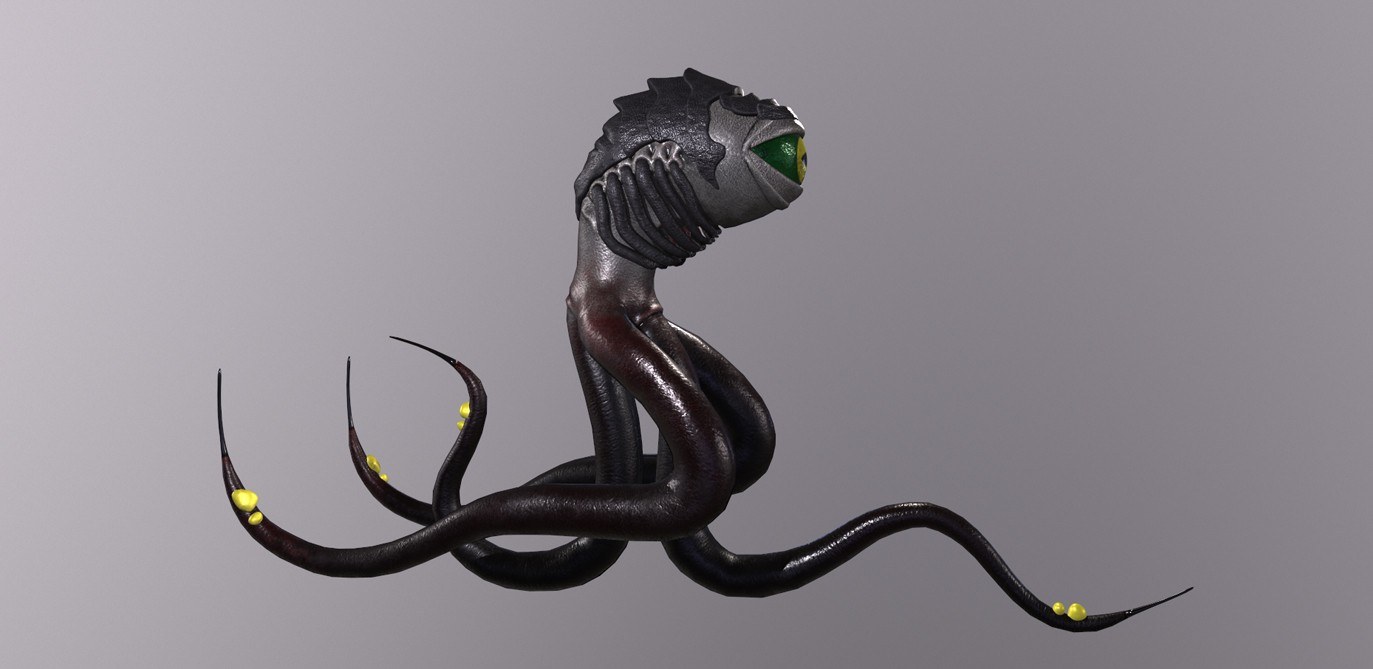
As a turn-based strategy and action RPG, Nomadland features crisp, high-quality graphics due to its engine, which is Unreal Engine 4. Conceptually, the gist of its gameplay revolves around controlling a squad of troops and moving them around hexagonal fields from an isometric perspective. Another notable gameplay element presupposes the integration of NFTs into this project because each weapon, creature, or armor is a token.
Players can earn NFTs as they fight in PvE or PvP mode with the ability to trade them on a marketplace, gaining financial profit from the gameplay. A critical point here wasn’t to bet on blockchain as the game’s foundation. Instead, our team struggled to focus on engaging gameplay itself and appealing environments but make the P2E model supplementary.
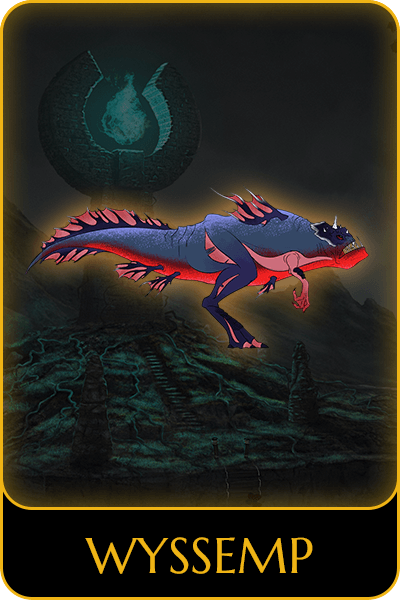
WHAT IS SO SPECIAL ABOUT NOMADLAND’S NFT?
Besides, our developers dedicated a considerable portion of inspiration to creating the following game aspects:
- The system of abilities for combat units;
- Gameplay balance and battle logic;
- Player base in a unique visual style;
- Inspiring backstory and thought-out world mythology;
- Hexagonal arena with props and environments;
- Weapon crafting mechanism;
- Token economy;
- Art for NFT and the system of their generation;
- Functional marketplace;
- Monster taming and domestication mechanic.
Gameplay screenshots

NFT Marketplace
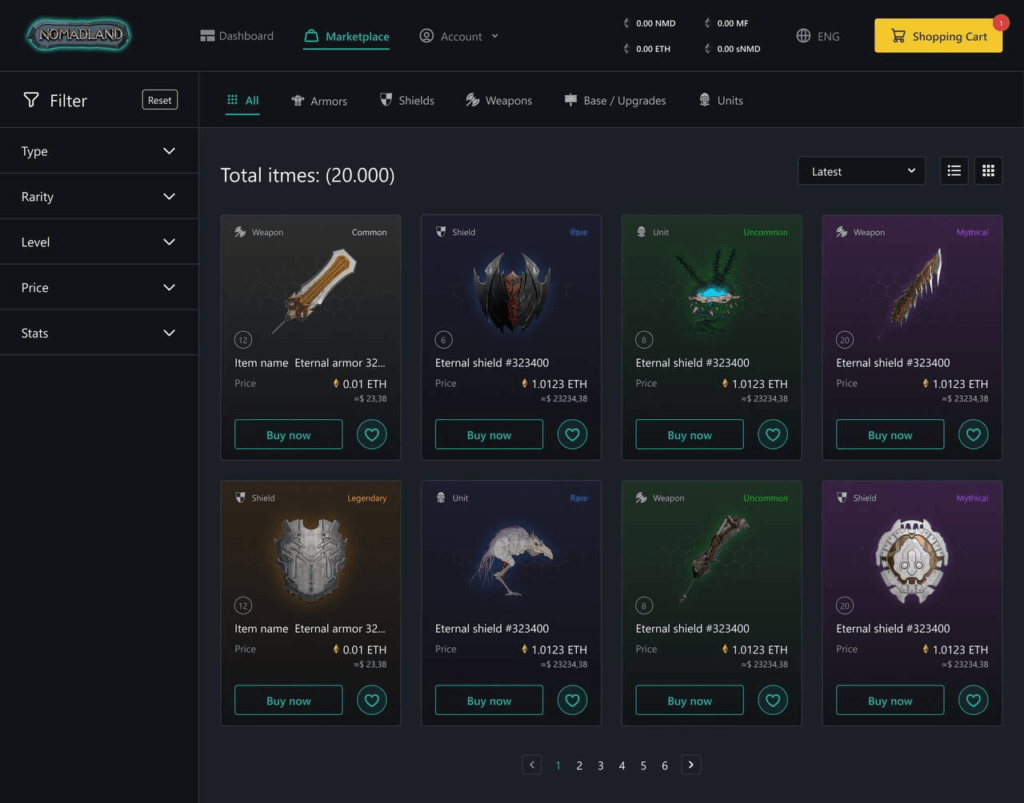
NFT Assets
Since Nomadland is a blockchain-based NFT game, the role of tokens is substantial yet not meant to become more significant than core gameplay. Although similar products are usually developed to emphasize exclusively long-term profit, this game has managed to combine old-school mechanics with a progressive system of non-fungible tokens.
The marketplace, where players can buy and sell the acquired tokens, is one of those features that facilitate the development of NFT games. Having a vast 3D world to explore and stunning environments to contemplate, players might forget about the NFT aspect of the game, regarding Nomadland just as an exciting adventure.

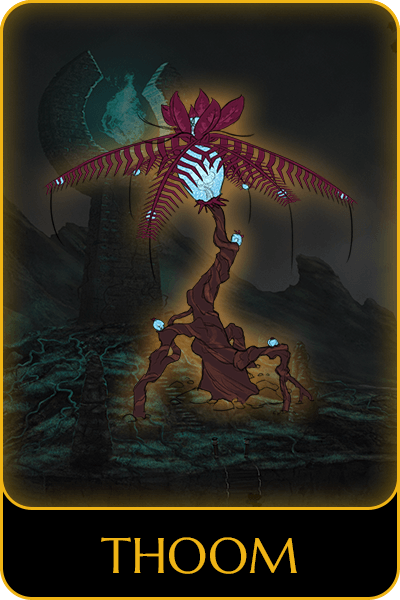
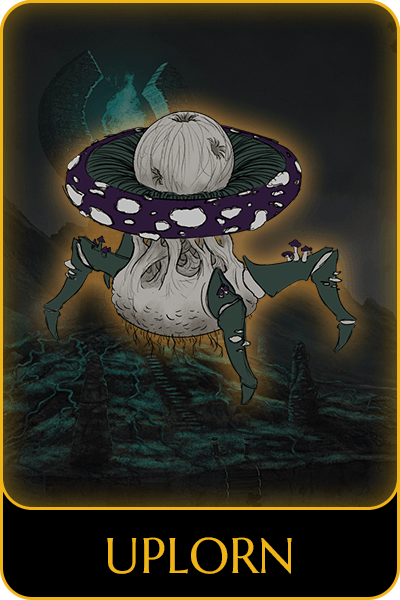

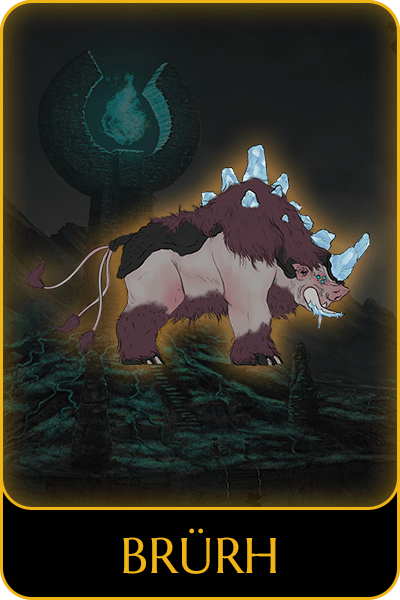

Game characters
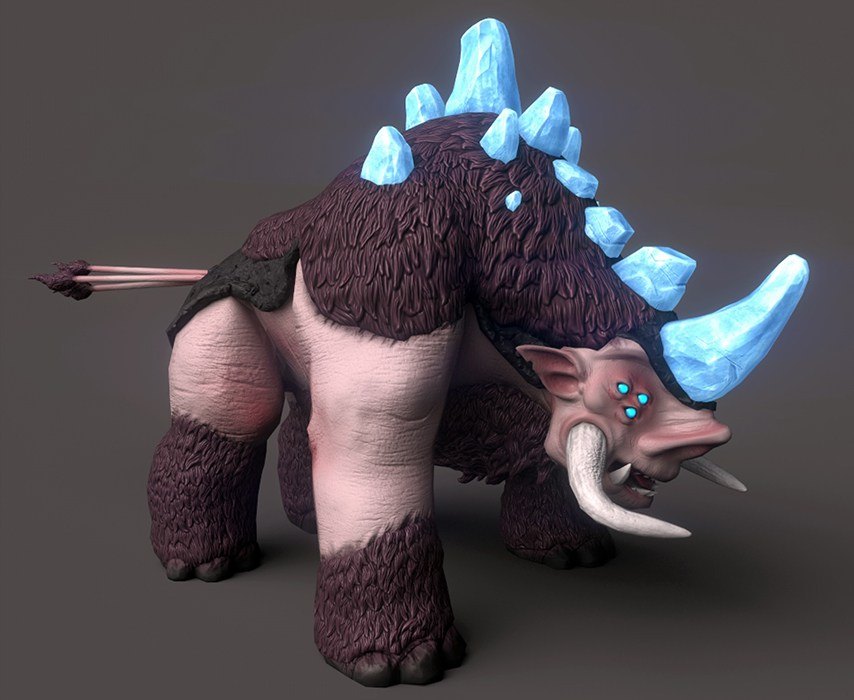
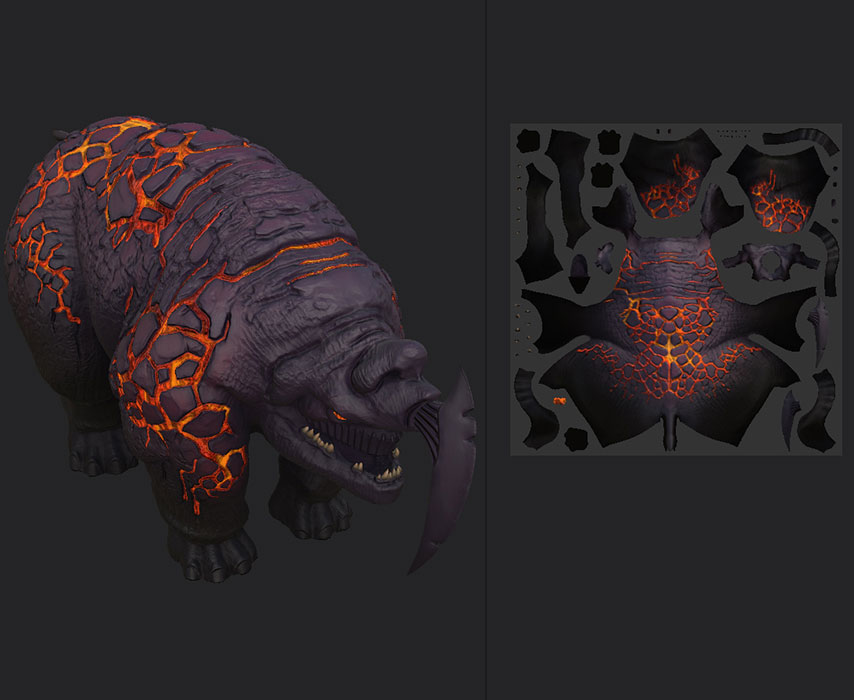






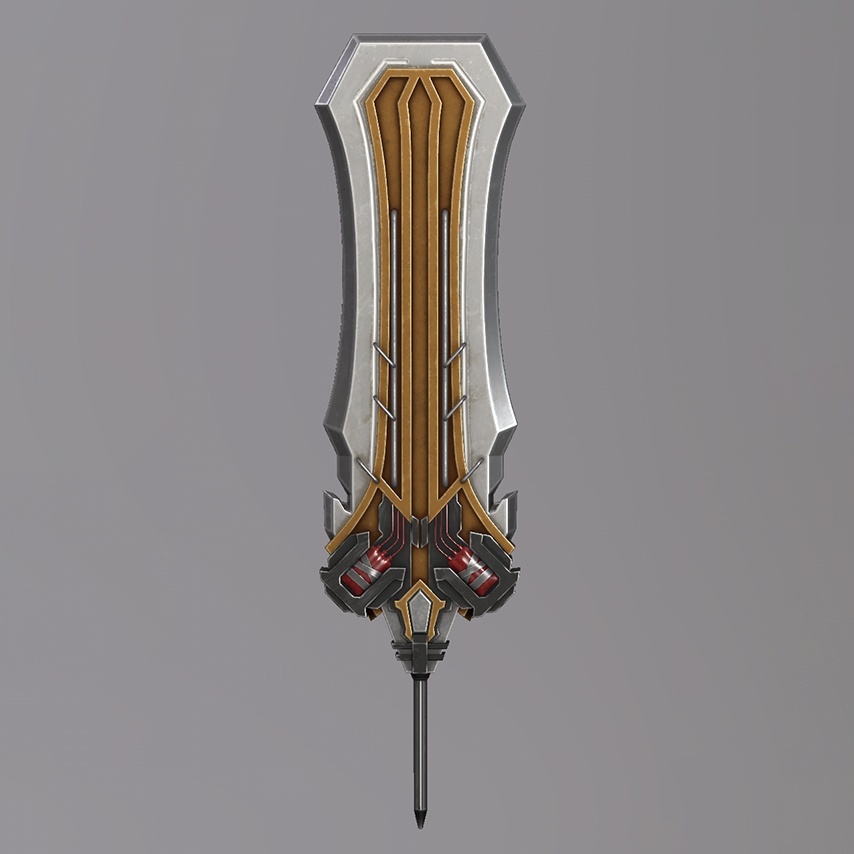
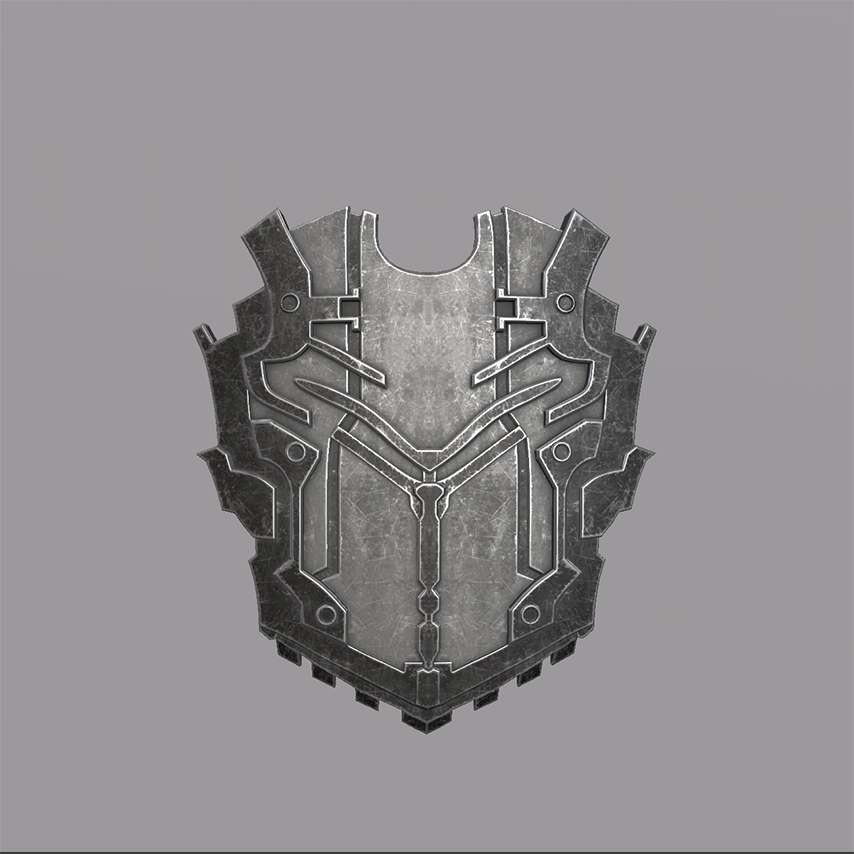
Weapons









Technology Stack
Aside from UI/UX, 3D art, animation, server-side programming, and blockchain integration, the core mission of the Game-Ace team implied creating an in-game token economy.
Developers employed Unreal Engine 4, its plugins, and other software to implement all the mechanics detailed in the GDD. Our specialists used Unreal’s system of visual scripting called Blueprints to create a ramification of customizations and level upgrade options.
Our team comprised an Unreal senior developer, 2 middle developers, 2 game designers, 1 business analyst, 2 project managers, 8 3D artists, 1 tech artist, 2 animators, and 1 sound designer. Game-Ace experts used many frameworks like Next.js for the back end, React.js for the admin panel, MongoDB as a database, and TrustWallet API for respective purposes.
GAME TRAILER

Results
Finally, the lion’s share of our work on this game can be concluded at least with the following theses:
- Nomadland has been perfectly optimized for PC as a play-to-earn NFT game;
- Game-Ace developed and finalized the game having only 2D concept art at hand;
- Our team has successfully integrated blockchain into Nomadland;
- We built the front- and back-end aspects of the project, including the online mode;
- All the coding in Unreal Engine was implemented by Game-Ace’s developers.