Simulation games are digital models of real or imagined systems. Players interact with these systems by making decisions, adjusting variables, and observing results. The goal is often to manage resources, solve problems, or understand how parts of the system affect each other. Simulation games do not rely on fast reflexes or action sequences. Instead, they ask players to think, plan, and adapt.
The popularity of simulation games continues to grow across different audiences. Some people use them to relax, while others treat them as serious tools for learning and improvement. Their designs are based on logic, rules, and feedback loops, which makes them useful beyond entertainment.
Business owners and decision-makers can find simulation games especially valuable. They show how small changes can lead to larger effects, and they create risk-free environments for testing ideas. Simulation games help users understand systems without the costs of real-world failure.
The article explains what is a simulation game, how simulation games work, and why simulation game development is useful for business thinking. It also gives clear examples to show their practical value.
What Are Simulation Games? — Answers You Wish You’d Known Earlier
Simulation games are a category of video games that copy real-world systems or environments. Players manage these systems by making choices, seeing the effects, and learning from the outcomes. The structure of simulation games depends on logical processes, not luck or speed. Some are used purely for fun, while others have serious uses in training or planning. For example, educational games for kids often include simulation elements to help them understand science, math, or social behavior.
From Flight Simulators to Virtual Cities: A Quick History of Simulation Games
The first simulation games appeared in military and academic settings. Flight simulators were used to train pilots without the risk of actual flight. These early tools helped people learn faster and avoid costly errors.

As computers became more available, simulations spread into entertainment. One of the first widely known examples was SimCity, released in 1989. It lets players build and manage a city, facing real problems like traffic, pollution, and budgets.

In the 2000s, The Sims became a new kind of simulation game. Instead of focusing on machines or cities, it modeled human behavior. Players controlled virtual people, managing their daily needs, emotions, and relationships.

Meanwhile, farming and vehicle simulators gained popularity in specific markets. Games like Farming Simulator and Euro Truck Simulator gave players realistic control over equipment and tasks, attracting people interested in detailed mechanics.
Roblox simulation games brought another change. Roblox is a platform where users can build and play games made by other users. Many of these are simple simulation games focused on jobs, life, or progress systems. For example, players can run a restaurant, take care of pets, or build a business. Roblox lowered the barrier for creating games, which led to a wide variety of user-generated simulation content.
Today, simulation games continue to expand. They are not limited to professional training or casual play. Many combine both elements, offering detailed systems that are still accessible to beginners. Across platforms and audiences, the appeal of simulation games stays strong because they provide feedback, control, and learning through trial and error.
Types of Simulation Games and Their Unique Mechanics
Simulation games fall into several distinct types. Each has its own mechanics and goals, shaped by what part of reality it tries to model. The following list outlines the major types found in today’s video game genres:
- Life simulation. Focuses on managing people or animals in daily activities, such as sleeping, eating, working, or socializing. Examples include The Sims and Animal Crossing.
- City-building simulation. Players plan and manage a city, dealing with zoning, traffic, economy, and public services. SimCity and Cities: Skylines are major titles of this type.
- Business simulation. Involves managing a company or economic system, often requiring attention to supply, demand, profit, and workforce. Games like Capitalism II or Game Dev Tycoon fit here.
- Vehicle simulation. Gives players realistic control of vehicles such as planes, trucks, trains, or ships. These games focus on precision and realistic physics, like Microsoft Flight Simulator or Train Simulator.
- Farming simulation. Centers on crop cycles, animal care, machinery, and weather. Farming Simulator is the most well-known example, with strong attention to realism.
- Medical simulation. Models healthcare environments, often used for both entertainment and training. Games like Surgeon Simulator offer a simplified version, while others are used in real medical schools.
- Sandbox or open-ended simulation. Lets players set their own goals in a free environment. Roblox simulation games often fall into this group, allowing for creativity and self-directed progress.
Each type offers a different way to explore systems and make decisions. Some games mix multiple types, leading to hybrid models that appeal to wider audiences.
How Simulation Games Mimic Real-World Systems
Simulation games use models to copy how real-world systems behave. These models follow rules that mirror how things work in daily life, whether it’s a traffic network, farm cycle, or economy. Players interact with variables, adjust inputs, and then see the output, which helps them understand cause and effect.
Game developers use systems thinking to build simulations. That means creating links between different game elements. For example, in a farming simulator, changing the weather can impact crop yield and profit. Higher wages might lead to happier workers but lower profit margins in a business simulation. These mechanics allow players to test strategies in a space where failure has no real cost.
Feedback loops are also common. People may leave if a player builds too many houses in a city simulator without enough jobs. That result creates pressure to fix the balance. Over time, the player learns how to keep systems stable.
Good simulation games also simplify complexity. They remove unnecessary details while keeping the important rules. This balance makes systems easier to understand while still teaching how they work in the real world.
Why Simulation Games Are More Than Just Play

Simulation games are used for more than fun. They improve problem-solving, focus, and decision-making by modeling real systems. For learners, they offer an active way to understand complex topics. In workplaces, some companies use gamification techniques from simulation games to improve training, planning, and engagement. Simulations also support testing without risk, helping users see the results of decisions before acting in real life. This is one reason why simulation games continue to grow in value across education, industry, and personal development.
Cognitive Engagement and Strategic Thinking in Sim Gameplay
Simulation games require constant attention to systems and patterns. Players must make choices, monitor outcomes, and revise strategies. This creates deep cognitive engagement that strengthens focus and problem-solving skills. Unlike action games, simulations reward careful planning rather than fast reactions.
Each game run provides a new opportunity to test ideas. In Cities: Skylines, for example, players need to manage traffic, zoning, pollution, and budgeting at once. Fixing one problem often creates another. Strategic thinking is essential to maintain balance across systems. Players learn to anticipate effects before making changes.
Time management and resource allocation are also key elements. Players must set priorities and plan ahead when managing a virtual business or a farm. These activities mirror real-world decision-making, especially under constraints.
Simulation games also encourage long-term thinking. Progress happens over time, and early decisions often affect the result. Players develop patience and persistence by working toward complex goals.
Because these games reward logic and analysis, they build habits that support planning in everyday tasks. The structured environments help sharpen thinking in ways that apply beyond gaming.
Training Through Simulation: A Tool for Real-World Preparedness
Simulation games are often used as training tools because they let people practice without real consequences. In aviation, pilots use flight simulators to learn how to handle emergencies.
Simulations help doctors and nurses prepare for surgeries or crisis scenarios in healthcare. They can test responses, practice procedures, and improve teamwork in a safe environment. Mistakes are part of learning, and simulation allows correction without harm.
In business, training simulations are used to teach management, finance, and operations. Trainees get to make decisions and see how those choices affect outcomes.
The military also uses simulations, where soldiers can prepare for complex missions using virtual environments. These tools improve reaction time, coordination, and planning under pressure.
For students, educational simulations can explain concepts through practice rather than theory. Instead of reading about supply chains, learners can run a virtual factory. That’s why gamification in education often includes simulation — it gives students direct control and instant feedback.
Need a quality simulation game? We’re in!
The Psychology Behind Simulation Games
Simulation games appeal to mental patterns that people use every day. They offer control, structure, and feedback, all of which support motivation. Many players enjoy solving problems, organizing systems, and learning from results. These features explain why simulation games are common in both entertainment and learning. Gamification in education uses similar tools to increase focus and improve understanding. The psychology behind simulation games shows that they meet real cognitive needs in a structured and engaging way.
Why We’re Drawn to Control and Complexity
People often choose simulation games because they offer more than just entertainment. These games give users control over detailed systems and provide challenges that require thinking and decision-making. The reasons behind this attraction are clear once we look at how the games are designed and how players respond to them.
The mix of freedom, structure, and learning gives players a meaningful experience that stays fresh over time. Rather than being passive entertainment, simulation games offer active engagement that satisfies both curiosity and the need to make decisions.
Decision-Making Under Pressure: Sim Games as Microcosms of Leadership
Simulation games often place players in roles that require leadership-level thinking. They must manage limited resources, handle unexpected events, and respond to changing conditions. These tasks mirror what leaders face in real life. The ability to make fast, informed decisions becomes essential for success in the game.
Pressure in simulation games usually comes from time limits, complex systems, or competing priorities. In Football Manager, for example, players must choose lineups, tactics, and transfers while also managing team morale. Mistakes affect results, and recovery requires both analysis and action. The stress created by the game forces players to think like real leaders — weighing short-term costs against long-term benefits.
Simulations encourage adaptive thinking. When one plan fails, players must quickly switch to another. Leadership involves that kind of flexibility. Staying with a failing strategy leads to loss. Games train players to recognize failure early and act.
Simulation games also teach risk management. Taking bold actions can bring high rewards, but poor timing or missing information can lead to setbacks. Learning when to act and when to wait is a core leadership skill that these games help build in a practical and repeatable way.
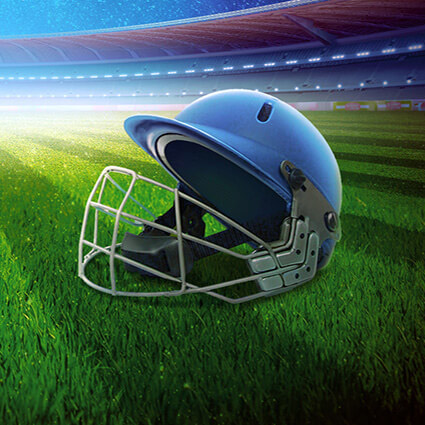
Step Into Cricket Manager, an MMO Sports Game by Game-Ace

Take control of your dream cricket club — train players, manage stadiums, and lead your team to glory. In this MMO simulator, Game-Ace developed the full game cycle, from concept art and UI to stadiums and characters. Leveraging server-side computing and mobile optimization, we delivered a fast-paced cricket experience for players worldwide.
Simulation Games and the Business Mindset
Simulation games encourage the kind of thinking that businesses value: strategic planning, resource management, and long-term forecasting. They show how systems work together and how small choices can affect larger outcomes. Business leaders can study simulation games to see how decisions, feedback, and user behavior interact.
Gamified Strategy: What Businesses Can Learn from Sim Game Design
Game design in simulations follows clear principles that can apply directly to business strategy. The following list explains some of the most useful ideas:
- Clear goals. Simulation games define objectives early and show progress toward them. Businesses benefit when they do the same for teams and projects.
- Feedback loops. Good games show results immediately after actions. This helps players learn quickly. In business, real-time feedback improves decision-making and team performance.
- Resource limits. Players in sim games must manage time, money, and materials. Companies also operate under constraints and must prioritize effectively.
- Balanced difficulty. Games challenge players without overwhelming them. The same applies to workplace goals — employees stay more engaged when the challenge matches their skill level.
- Iterative learning. Simulation games allow repeated trials. Businesses that build a test-and-learn culture can improve faster and adapt to change.
- User control. Players make meaningful choices in simulations. Empowering employees to make decisions increases motivation and ownership.
- System awareness. In games, one part of the system affects the whole. Businesses that understand connections between departments or processes perform more efficiently.
- Engagement through purpose. Simulations give players a reason to act. When teams understand the “why” behind a goal, motivation increases.
Businesses that adopt these ideas can improve planning, training, and innovation. Simulation games show how strong design leads to clear thinking and better results.
Risk Without Risk — Experimenting in Safe Environments
Simulation games allow experimentation in a space where failure costs nothing. Players can try different strategies, make mistakes, and restart as needed. Leaders often face situations where the wrong decision can waste time or money. Simulation environments provide a way to test ideas without those risks.
A supply chain simulator, for example, can model delays, shortages, or spikes in demand. Decision-makers can then see how small changes affect results, which helps them prepare for real problems without trial and error in live settings. In the same way, a pricing simulator can help teams understand how different prices affect customer behavior and profit margins.
The simulation also encourages bold thinking. When there is no penalty for failure, people are more likely to explore creative or unusual ideas. Businesses benefit when teams feel free to test new approaches and measure outcomes.
Success Stories: How Simulation Games Influence Real-World Innovation
In fields like urban planning, logistics, and defense, simulation-based design has led to real improvements in tools, strategies, and technologies. The following case studies show how well-designed simulation games can produce more than entertainment. They can support innovation, drive testing, and open new directions for both training and development.
Kerbal Space Program and Its Impact on STEM Engagement
Kerbal Space Program (KSP) is a space flight simulation game where players design and launch rockets, aiming to explore a realistic orbital physics environment. While the game uses fictional characters and humor, its mechanics are based on real astrodynamics, propulsion, and orbital transfer models. This made it a valuable tool not just for entertainment but for promoting STEM learning.
Educators and scientists noticed early on that KSP accurately represented concepts like delta-v, gravity assists, and fuel-to-mass ratios. Teachers began integrating it into physics and engineering classrooms to give students a hands-on way to test theories. Unlike diagrams or equations alone, the game lets players experiment and fail safely, then try again with better strategies.
NASA also took an interest. In 2015, the agency partnered with the game’s developers to release official educational content, including missions based on actual NASA projects. The collaboration aimed to inspire interest in aerospace and introduce players to real-world space exploration goals.
Many players credit KSP with inspiring them to study physics, engineering, or aerospace outside formal education. It lowers the barrier to understanding complex systems and gives players space (literally and figuratively) to apply them interactively.
KSP proves that simulation games can support real-world learning, especially when the systems modeled are accurate, transparent, and flexible enough to let users test theories through direct experimentation.
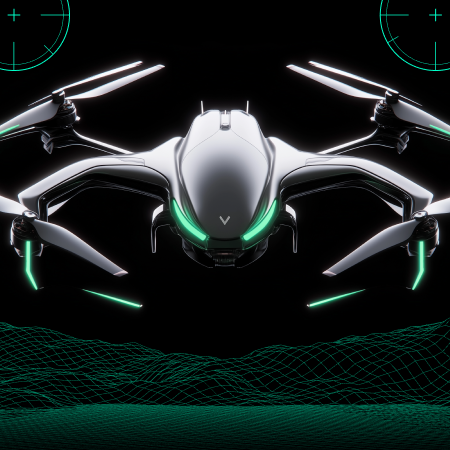
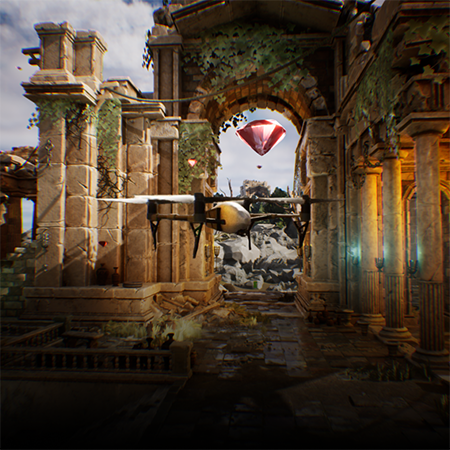
FPV Tank Hunter — A Prototype that Combines Precision, Strategy, and Realism
FPV Tank Hunter is a simulation game prototype that places players in control of a first-person drone tasked with navigating complex terrain and eliminating enemy tanks. Developed using Unreal Engine 5.5, the project combines realistic drone flight with high-stakes tactical gameplay.
The game centers on authentic FPV controls. Every movement simulates real drone navigation, informed by input from experienced drone operators. Signal coverage systems, wind physics, and real-time weather all affect drone handling. These layers add challenge and realism, forcing players to think, adapt, and act with precision.
What makes FPV Tank Hunter stand out is how its features align with real drone operations. Signal interference, visibility loss due to weather, and environmental obstacles simulate what real pilots face in complex field conditions. The strategic layer — choosing how to approach and eliminate tanks — adds a tactical depth that pushes players to analyze and plan under pressure.
The technology stack plays a key role. Unreal Engine 5.5 allowed the integration of advanced visual effects and physical simulations, including wind direction, signal degradation, and lighting changes. Blueprints and C++ were used to build reliable core mechanics quickly and efficiently.
The result is more than a game. FPV Tank Hunter demonstrates how simulation-based prototypes can serve both as immersive experiences and as proof-of-concept tools. It reflects the potential of simulation games in training, prototyping, and system design, where testing in real-world conditions would be too costly or dangerous.
The Future of Simulation Games: From Entertainment to Enterprise
Simulation games are becoming more advanced and more useful beyond personal entertainment. Improvements in graphics, physics, and AI make it easier to create systems that closely match real-life behavior. These developments open new possibilities for business, education, and technical training.
Game engines like Unreal Engine and Unity are no longer just for entertainment studios. Companies use them to create virtual environments for testing, planning, and employee training. For example, logistics teams can simulate warehouse layouts, while engineering teams can model equipment behavior under different conditions.
AI integration also plays a growing role. Games can now generate smarter responses to player actions, making training simulations more realistic. Shortly, these systems could support business simulations that adapt to a user’s choices in real time, giving more accurate feedback and deeper insight into decision-making.
Mixed reality and VR will also push simulation into new use cases. Pilots, doctors, and factory workers already use immersive training tools. As headsets become cheaper and software becomes more refined, simulation will be a regular part of workforce development, planning, and testing.
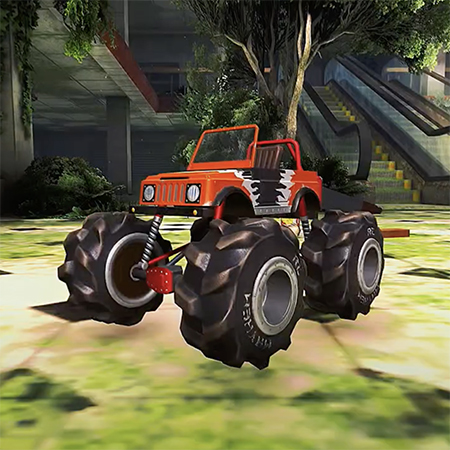
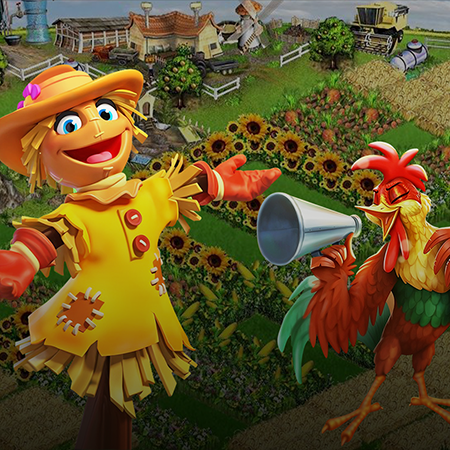
Welcome to Farmerama, a Casual Farming Simulator by Game-Ace

In this colorful farm-themed simulation, players cultivate crops, raise animals, and trade with fellow farmers to grow a thriving agricultural paradise. Game-Ace helped Bigpoint transition the game from Flash to Unity, enhancing performance, adding new mechanics, and preserving its legacy.
Developing Smarter Simulation Games with Game-Ace
Building a simulation game that serves a real purpose requires technical accuracy, responsive controls, and well-structured systems. Game-Ace is a custom game development company with experience in designing simulation games for training, planning, and commercial use. The team combines industry knowledge with advanced tools like Unreal Engine and Unity to deliver functional and visually strong products.
Each simulation is developed with clear goals in mind, whether it’s skill training, equipment testing, or strategic decision-making. Many organizations also adopt games for business to embed real-world decision contexts into their operational training. Clients receive support throughout the full development cycle, from early concept to final delivery. Previous projects include simulations for logistics, defense, and agriculture, each adapted to specific real-world tasks.
Anyone interested in simulation-based solutions can request a consultation or development estimate. To discuss your idea or get answers from our team, contact us through our official site. Game-Ace is ready to help you turn a concept into a working simulation that fits your practical needs.
 Engineering the Next Generation of Tower Defense Games
Engineering the Next Generation of Tower Defense Games  How to Turn Idle Game Development into a Scalable, Long-Term Revenue Product
How to Turn Idle Game Development into a Scalable, Long-Term Revenue Product  Key Trends Shaping Gamification in Recruitment for 2026 and Beyond
Key Trends Shaping Gamification in Recruitment for 2026 and Beyond  How to Create Crypto Casino Games the Right Way
How to Create Crypto Casino Games the Right Way  AI Recruitment Games: From Real-Time Assessments to Better Hiring Outcomes
AI Recruitment Games: From Real-Time Assessments to Better Hiring Outcomes