Game-based learning is no longer just an alternative approach. It’s a proven method for building real skills through interactive experiences. When designed correctly, educational games improve attention, increase retention, and create measurable outcomes across various industries.
More companies and institutions now adopt serious game development to train employees, engage students, and improve long-term performance. Unlike passive content or one-way instruction, game-based learning gives users an active role. They complete tasks, solve problems, and apply knowledge in real-time situations.
Serious game development focuses on purpose. Every feature, challenge, and response has a clear goal for learning outcomes. Whether used in healthcare, manufacturing, or corporate settings, these games target specific skills and provide structured feedback. The format is flexible enough to support team collaboration, individual decision-making, or performance benchmarking.
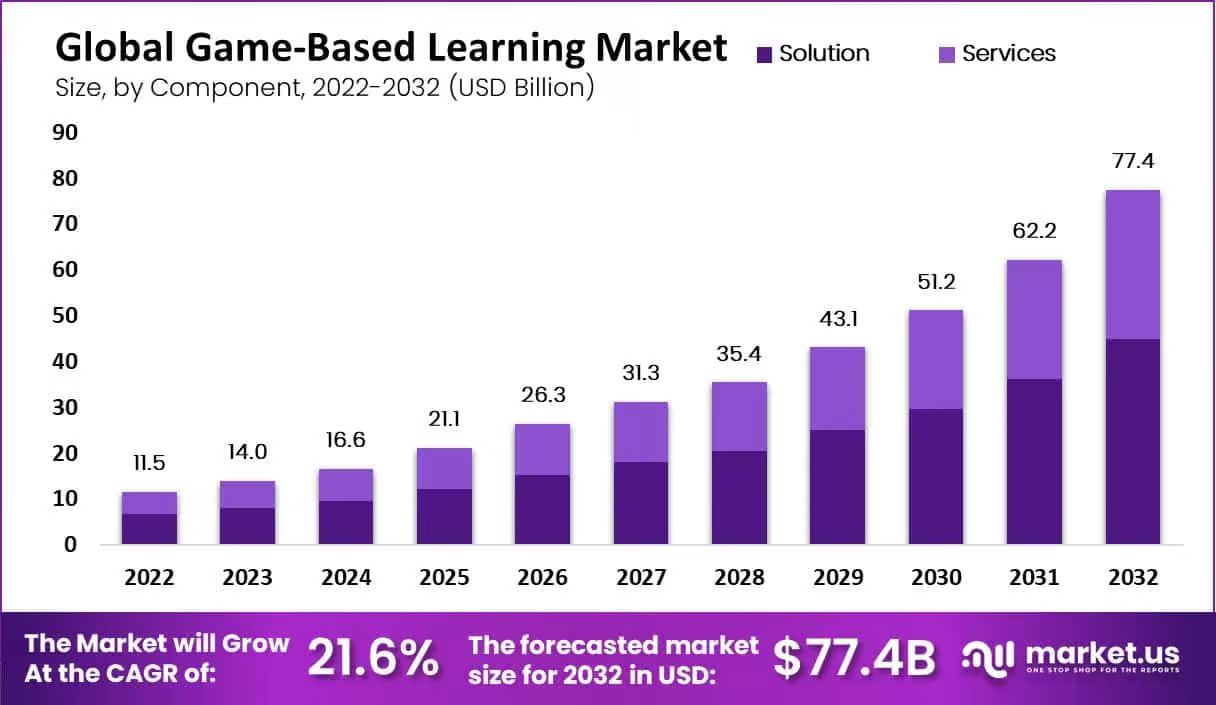
The growing interest in game-based learning comes from its ability to make training more relevant and memorable. Users apply knowledge faster and recall it longer. Organizations benefit from better engagement and data on skill development. With the right design, serious game development produces training that works.
What Is Game-Based Learning and How Does It Work?
Game-based learning is a structured approach that uses games to support the acquisition of specific knowledge or skills. It differs from casual gameplay by focusing on learning objectives, task completion, and real-time feedback.
Unlike entertainment games, serious games are built with clear instructional goals and often simulate real situations. Users learn by solving problems, making decisions, and observing consequences, all within a controlled environment. The method is effective for young learners and professionals, offering active participation instead of passive content consumption.
Core Principles Behind Game-Based Learning
Game-based learning uses specific principles that make it different from other training methods. Each principle directly supports knowledge transfer and long-term retention.
- Clear objectives. Every game is designed around measurable learning goals.
- Immediate feedback. Users receive input during the activity, helping correct mistakes early.
- Progress tracking. Learners can see their own development over time.
- Repetition with variation. Key concepts are practiced in different contexts to improve understanding.
- Safe failure. Users can experiment and learn from mistakes without real-world risks.
- Motivation through rewards. Achievements and progress markers keep engagement high.
- Contextual learning. Skills are practiced within realistic environments.
- Adaptive difficulty. Tasks become more challenging as the user improves.
Gamification in learning applies these elements in structured formats, adding challenges and milestones to maintain focus. Unlike basic content delivery, this approach builds active involvement, which leads to stronger memory and better real-world application.
Game-based learning works best when tied to practical use cases. It’s not about playing for fun but learning through action. This approach is especially relevant in games for business, where learning must generate measurable metrics, not just engagement. Every principle exists to build useful habits and skills that can be transferred to daily performance.
Types of Game Mechanics Commonly Used
Different mechanics shape how users interact with game-based content. Below are the most commonly used mechanics in educational settings.
- Points and scoring. Users earn points for completing tasks correctly.
- Levels. Structured stages provide a clear learning path and increasing difficulty.
- Challenges. Tasks test specific skills and encourage critical thinking.
- Time limits. Adds urgency to tasks and improves focus under pressure.
- Feedback systems. Visual or audio responses indicate success or failure.
- Badges and achievements. Recognize progress and build motivation.
- Simulation-based tasks. Replicate real-world scenarios for practical experience.
- Leaderboards. Encourage healthy competition and peer comparison.
- Quests or missions. Provide goals and a clear sense of purpose.
- Branching paths. Let users explore different outcomes based on their decisions.
These mechanics aren't used randomly. They match the learning goals, user profile, and context of use. When selected carefully, they turn complex training into engaging and productive experiences.
Distinguishing Game-Based Learning from Traditional eLearning
Game-based learning differs from traditional eLearning in both format and impact. Standard eLearning often involves reading content, watching videos, and taking quizzes. In contrast, game-based methods are built around interaction and problem-solving.
Critical differences include:
- Learning through doing. Game-based approaches use tasks and challenges, not just passive reading.
- Engagement style. Games maintain attention through rewards and progression rather than linear modules.
- Motivation model. Users are driven by achievement and exploration, not just completion rates.
- Feedback speed. Game-based systems give instant feedback during the activity, not after tests.
- Retention rates. Skills practiced in games stick better due to active participation.
- Personalization. Games often adapt based on performance; traditional methods do not.
- Reusability. Game scenarios can be replayed with different strategies, reinforcing the lesson.
Educational games for kids are an excellent example. A math quiz in eLearning might ask for the correct answers, but a game might involve building structures using calculations. That difference in approach creates a more profound understanding and interest.
Game-based learning is more than a visual update to traditional content. It changes how users interact with information, making the learning process more direct and lasting.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Game-Based Learning

Game-based learning offers multiple benefits but also comes with specific challenges. It increases engagement, improves knowledge retention, and allows for skill-building in safe environments. At the same time, it requires careful planning, adequate technology, and skilled development teams. The method works best when organizations match it with realistic goals, timelines, and user expectations. Understanding both the strengths and weaknesses helps in making informed decisions about implementation.
Key Strengths: Motivation, Feedback Loops, and Personalization
Game-based learning drives motivation by involving users in tasks where their actions lead to measurable outcomes. Unlike static learning formats, it gives people control over their progress.
- Personal goal setting. Games allow users to set their own pace and revisit areas as needed.
- Instant feedback. Learners receive direct responses to their actions, which helps them adjust quickly.
- High engagement. Game elements such as points, levels, and rewards sustain attention over more extended periods.
- Real-world application. Simulated environments help learners apply knowledge in contexts they can recognize.
- Autonomy. Players explore different approaches to solve problems, building independence.
- Personalization. The difficulty, content flow, and task types can adjust in real time based on performance.
Gamification in education uses these strengths to support individual learning needs and improve outcomes. With the right design, users feel challenged but not overwhelmed, which helps them progress steadily. The more the game aligns with actual skills, the more likely it will translate into real improvement. Sound feedback systems and adaptive learning paths are key to this success.
Limitations: Cost of Development and Technical Requirements
Gamification in education only works when infrastructure supports it. Even the best-designed games will face barriers without enough devices, storage, or IT support. Organizations need to weigh these factors before committing. In many cases, starting with a pilot version or simplified format helps manage risk while exploring the benefits.
- High development costs. Serious games need specialized design, testing, and production.
- Long timelines. Quality game-based training takes time to plan and build.
- Technical demands. Games often require specific devices, operating systems, or software updates.
- Ongoing maintenance. Bugs, content updates, and user feedback require continuous support.
- User readiness. Some learners are unfamiliar with interactive tools or may lack access to stable internet.
- Compatibility issues. Not all learning management systems support game-based formats easily.
Despite strong benefits, game-based learning has limitations, mostly related to logistics and technical barriers.
Balancing Fun with Learning Objectives
Creating effective game-based learning means ensuring that entertainment does not overshadow the instructional goal. Fun is useful, but not the purpose on its own.
- Clear objectives first. Developers must start with the learning outcomes, not the game mechanics.
- Task relevance. Every action in the game should contribute to the knowledge or skill being taught.
- No empty challenges. Avoid puzzles or levels that add difficulty without teaching anything new.
- Limit distractions. Graphics, audio, and game flow must enhance, not interrupt, the lesson.
- Progress aligned with skills. Learners should advance by mastering content, not just earning points.
- Structured guidance. Help must be available when users are stuck, not just failure loops.
Games that are fun but content-light do not produce long-term value. On the other hand, overly complex tasks can frustrate users. The right balance supports learning without reducing engagement. Every game-based learning activity should answer one question: what will the user know or do better after this? That answer must guide every design choice.
Haiku Serious Game: Elevating Cybersecurity Awareness Through Play

Haiku is a serious game that trains users in cybersecurity through hands-on challenges and immersive mechanics. Game-Ace enhanced its interface, performance, and usability to improve engagement and learning. Explore how we helped turn complex concepts into interactive training.
Gamification vs. Game-Based Learning — Why the Difference Matters
| Gamification | Game-Based Learning |
| Adds game-inspired elements (points, badges, rankings) to existing lessons without changing the lesson structure. | Uses full games built around specific learning goals and outcomes. |
| Driven by external rewards. Learners stay motivated to earn grades, unlock features, or win prizes. | Driven by internal motivation. Users engage because they enjoy the process and learn actively. |
| Lesson stays the same. Only the layer of interactivity is added to improve engagement. | Content is shaped around the game. Every part of the gameplay is tied to a learning goal. |
| Assessment happens outside the activity. Quizzes or evaluations are separate from the gamified content. | Assessment is integrated. Player performance and choices reflect real-time learning. |
Gamification tweaks the way learners interact with existing material. Game-based learning builds the learning experience from the ground up using games. Both have their place, but their impact and structure differ entirely.
Definition and Use Cases of Gamification
Gamification is the practice of applying game-like features to non-game activities. It doesn’t use full games but borrows their mechanics, such as points, badges, leaderboards, and challenges, to make learning or work more engaging. The goal is to influence behavior, increase motivation, and drive participation in otherwise routine tasks.
Common use cases include:
- Online courses. Adding rewards and completion tracking to keep learners engaged.
- Corporate training. Encouraging employee participation in compliance modules.
- Health and fitness apps. Motivating users with streaks, badges, and social comparison.
- Customer loyalty programs. Rewarding purchases and engagement with points systems.
Gamification is effective when users need encouragement to complete repetitive or optional activities. It’s often used to increase short-term motivation and support consistent participation.
Side-by-Side Comparison: Goals, Tools, and Outcomes
Gamification and game-based learning differ in purpose, tools, and how they affect the user. Gamification aims to increase motivation and engagement. It uses tools like points, badges, leaderboards, and timers. Users complete tasks to earn rewards, but learning happens through standard content. The approach is indirect, added on top of existing material to keep people active. The typical result is higher participation, not necessarily deeper understanding.
Game-based learning, on the other hand, focuses on teaching specific skills or knowledge. It uses simulations, branching scenarios, missions, and feedback systems to create real learning experiences. Users solve problems, make decisions, and learn by doing. Such an approach is direct and fully built into the learning process. The goal is to help learners apply what they’ve learned, not just complete tasks. Each method supports different outcomes. Gamification encourages users to stay involved, while game-based learning builds understanding through action.
When to Use Each Approach
Use gamification to make existing content more engaging. It's useful for tasks that don't require deep understanding but benefit from higher completion rates, such as onboarding, surveys, or progress tracking.
Game-based learning works best when learners must master concepts, make decisions, or apply knowledge. It's instrumental in complex subjects like safety training, finance, or healthcare
If you're exploring how to make an educational game, start by identifying the learning objectives. Then, decide whether the best fit is a complete learning experience (game-based learning) or a gamified layer on top of your content.
Use gamification if:
- You have limited resources or time.
- The goal is short-term engagement.
Use game-based learning if:
- You want lasting skill development.
- The learning outcome requires practice and feedback.
Types of Game-Based Learning
Game-based learning includes a wide range of formats. Each type supports different skills and learning outcomes. Choosing the right type depends on your goals, audience, and content.
Card games
Card games are helpful for practicing memory, strategy, and concept recall. They often involve matching terms, answering questions, or solving problems under time limits. These games work well in classrooms and workshops, especially for reviewing material. They’re easy to set up, flexible, and promote learner interaction.
Board games
Board games combine strategy, planning, and knowledge application. Players often move pieces, draw cards, or complete challenges based on rules tied to learning topics. These games support group learning and build communication skills. They're well-suited for training sessions, classrooms, and team-building environments.
Simulation games
Simulation games replicate real-life scenarios. Users interact with systems or situations that mimic actual roles, tasks, or environments. They are widely used in medical, aviation, and industrial training. Learners gain practical experience by making decisions and observing consequences in a risk-free space.
Word games
Word games improve vocabulary, spelling, and language structure. Learners may form words, identify definitions, or rearrange terms. These games are often used in language learning and early education. They can be competitive or collaborative and easily adapt to different skill levels.
Puzzle games
Puzzle games challenge learners to solve logical or spatial problems. They strengthen reasoning, sequencing, and problem-solving skills. Puzzles can be math-based, visual, or conceptual. These games work across age groups and are commonly used in STEM education and cognitive training.
Video games
Video games in education involve interactive digital environments where users complete tasks tied to learning objectives. They often include storytelling, progress tracking, and instant feedback. These games are engaging and scalable, making them suitable for corporate training, schools, and remote learning.
Role-playing games (RPGs)
Role-playing games allow learners to take on specific roles and interact within a structured scenario. Players practice communication, decision-making, and empathy. RPGs are often used in leadership training, conflict resolution, and customer service education. They promote active learning and group participation.
Business Benefits That Make Game-Based Learning a Smart Investment

Game-based learning offers more than educational value. It supports measurable business goals such as improved employee performance, reduced training costs, and faster onboarding. Companies benefit from better knowledge retention, higher engagement, and scalable training methods. With the right design, game-based learning provides lasting value and practical outcomes across departments.
Higher Retention and Engagement Rates
Employees often forget traditional training content shortly after a session ends. Game-based learning helps solve that issue by increasing retention through active participation. Instead of reading slides or listening to lectures, learners complete tasks, solve problems, and receive immediate feedback. That interaction makes content easier to remember and apply.
Game elements such as levels, progress tracking, and challenges maintain attention throughout the session. Users feel more involved and take an active role in their development. This leads to longer focus times and better completion rates.
Compared to standard methods, game-based approaches reduce passive learning and improve knowledge transfer. Teams that stay engaged are more likely to remember the training and use it in their daily work. For companies, this means fewer repeated sessions and better overall performance outcomes from a single investment in training.
Cost-Efficiency Over Time
Although game-based learning can require more time and resources upfront, it becomes cost-effective in the long run. Once developed, digital training programs are reusable, scalable, and easy to update. There’s no need to schedule multiple live sessions or repeatedly bring in instructors.
Companies save on travel, printing, venue rentals, and time away from core duties. Learners complete training at their own pace, reducing downtime and allowing flexible integration into work routines.
Digital tools also provide detailed analytics. Managers can track progress, identify gaps, and fine-tune programs without starting from scratch. Unlike traditional methods, game-based training remains relevant and accessible with minor updates.
The return on investment grows with each use for organizations with high turnover or large teams. A well-designed serious game serves hundreds of employees without additional delivery costs, making it a scalable and budget-friendly solution over time.
Practical Skill Development Through Simulation
Game-based learning supports real skill development by simulating tasks and environments that employees face on the job. Learners interact with realistic scenarios, make decisions, and deal with consequences in a safe, virtual space, preparing them for actual responsibilities without the risks of real-world mistakes.
Simulation-based learning builds confidence. Users practice procedures, respond to challenges, and refine techniques in a structured way. Whether it's customer service, technical repair, or safety procedures, they gain experience through hands-on interaction.
The learning process becomes more meaningful when tied to daily work. Employees understand the theory and know how to apply it under pressure, reducing errors and shortening the learning curve once they take on the role in real life.
Organizations benefit from a workforce that's not just trained but job-ready. Fewer mistakes, better compliance, and faster ramp-up times all contribute to smoother operations and improved team performance.
Game-Based Learning Examples Across Industries
Game-based learning supports practical training in various fields, from technical industries to customer-facing roles. Companies use it to improve safety, accuracy, and efficiency. For frontline workers or skilled professionals, serious games deliver targeted knowledge in a structured, interactive format. Even Roblox educational games now support custom training environments across sectors.
Compliance Training in Manufacturing and Energy
Compliance training is critical in sectors like manufacturing and energy, where mistakes can lead to injury, shutdowns, or legal issues. Game-based learning helps employees understand and follow complex regulations by simulating real workplace conditions.
Instead of reading manuals, learners interact with virtual environments that present typical compliance challenges. They inspect machinery, follow safety steps, and react to potential hazards, all while receiving feedback. These simulations make remembering procedures easier and understanding why each rule matters.
Key topics covered include lockout/tagout procedures, hazard identification, equipment checks, and emergency protocols. Repeating these tasks in a virtual setting helps reinforce correct behavior without risk.
This format supports quick onboarding and helps maintain standards across locations. Teams complete training at their own pace, and managers can track progress through analytics. The result is better compliance, fewer accidents, and lower training costs through a controlled, repeatable learning format.
Sales and Product Training in Retail
Retail employees need fast, effective training to understand product features, customer service protocols, and sales techniques. Game-based learning meets that need by turning training into structured challenges that mirror real store interactions.
A serious game might include customer scenarios where learners must recommend products, manage objections, or process returns correctly. Every decision impacts outcomes, allowing users to learn from mistakes and improve their responses.
Interactive tasks also help staff stay up to date on new product lines. They explore items virtually, compare options, and answer questions within a guided system that tracks progress. Points, rewards, and time-based challenges make the experience more engaging.
Managers benefit from real-time insights into how well staff understand the material. This data supports targeted coaching and ensures each team member is ready to deliver consistent service. By replacing static materials with simulated sales interactions, retail companies reduce training time and improve customer satisfaction across locations.
Healthcare Simulations for Medical Professionals
Medical professionals must learn and retain detailed procedures under pressure. Game-based learning helps by providing hands-on simulations that replicate real clinical environments. This allows doctors, nurses, and technicians to practice in realistic settings without endangering patients.
A typical healthcare training game might simulate patient intake, emergency response, or medication administration. Users make time-sensitive decisions, interpret test results, and follow clinical protocols. The system offers feedback and tracks performance to reinforce correct actions.
Unlike lecture-based sessions, simulations improve retention through active decision-making. They also allow for repetition, helping learners refine skills before applying them in real-world settings. Complications and branching scenarios prepare staff for unexpected outcomes.
Hospitals and medical schools use serious games to train both new hires and experienced staff. Topics include surgical procedures, infection control, diagnostics, and team coordination. The approach improves confidence, accuracy, and response times while reducing costly mistakes. Game-based learning in healthcare supports higher standards of care through repeated, low-risk practice.
FPV Tank Hunter: Drone Warfare Meets Tactical Gameplay

FPV Tank Hunter is a drone warfare prototype developed in Unreal Engine 5.5, featuring precision drone control, dynamic weather, and strategic tank combat. Game-Ace created a polished, immersive experience with advanced physics and authentic feedback. Read more to see how we turn concepts into cutting-edge simulations.
Overcoming the Challenges of Game-Based Learning
Implementing game-based learning can be complex without the right strategy. Common obstacles include unclear goals, scalability issues, and limited ways to track progress. Addressing these challenges requires planning, the right technology, and a strong connection between gameplay and learning outcomes. With proper execution, these barriers can be managed effectively.
Aligning Learning Objectives With Gameplay
A common issue in game-based learning is when the gameplay becomes more engaging than educational. To ensure effectiveness, every game element must support a clear learning goal. Users might enjoy the experience without this connection but retain little relevant knowledge.
To align gameplay with learning objectives:
- Define clear outcomes. Identify exactly what learners should know or be able to do after playing.
- Choose relevant mechanics. Select game features that directly support the content, such as branching scenarios for decision-making training.
- Avoid unnecessary challenges. Remove mechanics that distract from or complicate the learning goal.
- Test with real users. Use pilot groups to validate whether the gameplay reinforces the target skills.
- Use feedback loops. Design the game to correct mistakes in real time and reinforce correct behavior.
- Tie progress to learning. Ensure users advance only after demonstrating knowledge or skill improvement.
When the game experience is built around what users need to learn, engagement and retention improve. Learning becomes active, goal-oriented, and easy to measure.
Ensuring Scalability Across Teams or Locations
Scalability is a major concern for large organizations that want to use game-based learning across departments or countries. To function effectively at scale, a training solution must be adaptable and accessible.
To support scalability:
- Use cloud-based platforms. These allow remote access and centralized updates across locations.
- Ensure device compatibility. Games should work on various devices — PCs, tablets, and mobile phones.
- Design modular content. Break down the game into smaller sections that can be reused or updated independently.
- Provide language options. Include translations or localization support for international teams.
- Enable admin controls. Let managers assign, monitor, and modify training paths without developer support.
- Track progress centrally. Use dashboards and analytics tools to view results across teams in real time.
A scalable game-based training program minimizes repeated work, reduces deployment time, and keeps the learning consistent. It also allows rapid adjustments when company policies, tools, or goals evolve.
Measuring ROI and Performance Improvements
Proving the value of game-based learning requires clear metrics. Without data, it’s hard to know if the training works, how users respond, or whether skills improve. Measuring ROI starts with tracking the right things.
To measure impact effectively:
- Set benchmarks. Identify baseline knowledge or performance before training begins.
- Track in-game behavior. Monitor completion rates, decision paths, and time spent per task.
- Assess post-training outcomes. Compare performance before and after the learning experience.
- Use built-in assessments. Include quizzes or scenario outcomes to check learning in real time.
- Gather user feedback. Survey learners on the clarity, difficulty, and usefulness of the game.
- Compare KPIs. Look at real-world metrics like productivity, error rates, or compliance scores after training.
Strong ROI comes from more than participation. The best game-based learning systems connect player actions to real knowledge, behavior, or results changes. When tracked correctly, the data shows exactly where the value was created.
How to Choose the Right Platform and Partner for Implementation
Selecting the right tools and development partner is essential to launching an effective game-based learning solution. The wrong platform can limit flexibility, while a poor match with a vendor may delay progress. Focus on functionality, support, and alignment with your training goals to ensure long-term success.
Features to Look for in Game-Based Learning Platforms
Not every platform fits every organization. The right platform should support the technical needs of your team while providing features that directly enhance learning outcomes.
Some features to prioritize:
- User-friendly interface. A clean and intuitive design helps both admins and learners stay focused.
- Analytics and tracking. Built-in dashboards allow you to monitor progress and evaluate performance.
- Custom content support. The ability to add or modify learning content based on internal needs.
- Mobile and desktop compatibility. Learners should be able to train on any common device.
- Interactive feedback. Instant responses to actions help reinforce learning as it happens.
- Scalability options. The platform must accommodate growth across locations or departments.
- Integration with LMS. Smooth data sharing with existing learning management systems.
- Multilingual support. For organizations with global teams, language flexibility is essential.
- Offline access. Critical in regions with unstable internet or field-based operations.
- Security standards. Data encryption and user privacy controls should meet company policies.
Choosing a platform with these features ensures smoother implementation, easier management, and better learner engagement from day one.
Custom vs. Off-the-Shelf Solutions
| Aspect | Custom Solution | Off-the-Shelf Solution |
| Development time | Longer, requires detailed planning and production. | Immediate or short setup time. |
| Upfront cost | Higher initial investment. | Lower starting cost. |
| Content alignment | Fully tailored to your specific goals and processes. | May not match all training needs. |
| Flexibility | High — features and design can adapt to your organization. | Limited customization. |
| Scalability | Built for your internal systems and growth plans. | May require adjustments to scale effectively. |
| User experience | Designed for your audience, roles, and technical conditions. | Generic experience suited to broader use cases. |
| Maintenance and updates | Requires ongoing collaboration with the developer. | Vendor usually handles updates. |
| Long-term value | High if aligned with evolving business goals. | May decrease as needs change. |
Hopster’s Alphabet Hotel: Gamified Literacy for Preschoolers

Hopster’s Alphabet Hotel is an educational game designed to help preschoolers recognize letters and build reading skills through playful, character-driven mini-games. Developed with Hopster, Game-Ace brought this title to life by creating 3D content, animations, and engaging mechanics tailored to young learners.
Critical Questions to Ask Before Deployment
Before launching a game-based learning program, evaluating the solution and your organization’s readiness is essential.
-
What are the specific learning outcomes we want to achieve?
Clear goals help guide the design and evaluation process.
-
Does the platform support all devices used by our teams?
Accessibility across desktop and mobile is essential for full adoption.
-
How will we track learner progress and performance?
The platform must include analytics to measure engagement and learning success.
-
Is the content customizable to reflect our processes or scenarios?
Real-world relevance increases learner engagement and retention.
-
What technical support is available during and after implementation?
Reliable support reduces downtime and ensures smooth usage.
-
Can the solution scale with our team as we grow?
A good platform should handle more users, content, and locations over time.
-
Does the solution integrate with our existing LMS or HR tools?
Integration streamlines reporting and reduces manual work.
-
How secure is the platform in terms of data protection?
Ensure it meets internal security requirements and industry standards.
-
What’s the total cost over the next 1–3 years?
Consider licensing, maintenance, and update fees.
-
Who will manage the training content and updates internally?
Define team roles to keep the program current and effective.
Contact pros in game-based learning for better outcomes.
Turning Engagement into Long-Term Results with Game-Ace
Training is only effective if it leads to real change. At Game-Ace, we focus on building game-based learning solutions that engage users and drive measurable improvement in knowledge and performance. As a custom game development company, we tailor each project to your industry, goals, and team structure.
We go beyond visuals and gamification. Our team helps align your training content with user behavior, integrates performance tracking, and ensures scalability from day one. You get a partner who understands training at scale.
Are you ready to create training that sticks? Contact us to discuss your project and discover how serious games can deliver real results across your organization.
 The Architect’s Dilemma: Engineering the Next Generation of Tower Defense
The Architect’s Dilemma: Engineering the Next Generation of Tower Defense  How to Turn Idle Game Development into a Scalable, Long-Term Revenue Product
How to Turn Idle Game Development into a Scalable, Long-Term Revenue Product  Key Trends Shaping Gamification in Recruitment for 2026 and Beyond
Key Trends Shaping Gamification in Recruitment for 2026 and Beyond  How to Create Crypto Casino Games the Right Way
How to Create Crypto Casino Games the Right Way  AI Recruitment Games: From Real-Time Assessments to Better Hiring Outcomes
AI Recruitment Games: From Real-Time Assessments to Better Hiring Outcomes